A field set is a grouping of fields, you can use the field set in visualforce page to display group of fields in that page dynamically. No need to do code modifications to the page, In field set only you can add, remove & reorder fields. Generally these field sets are useful in managed packages. If the page is added to a managed package, administrators can add, remove, or reorder fields in a field set to modify the fields presented on the Visualforce page without modifying any code. Field sets are available for Visualforce pages on API version 21.0 or above. You can have up to 50 field sets referenced on a single page.
Here the below example is on a custom object “Project__c”.
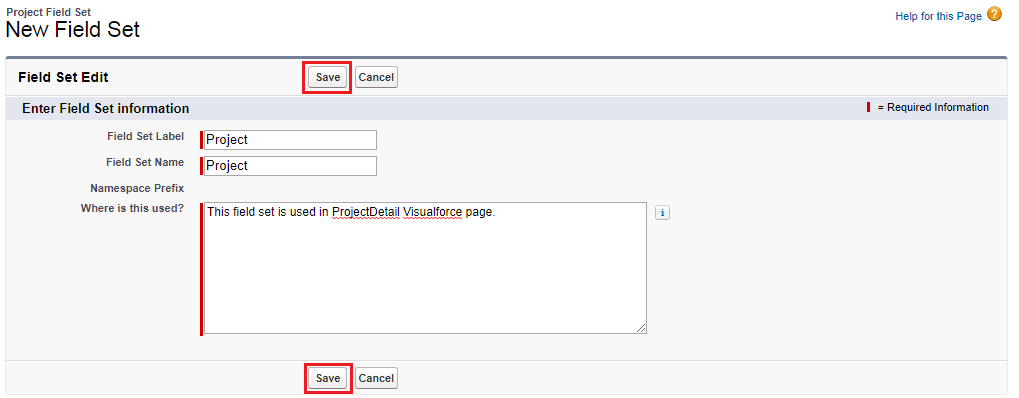
To create a field set, go to object.
Create field set by clicking on new button in field set section.

Enter required fields and save.
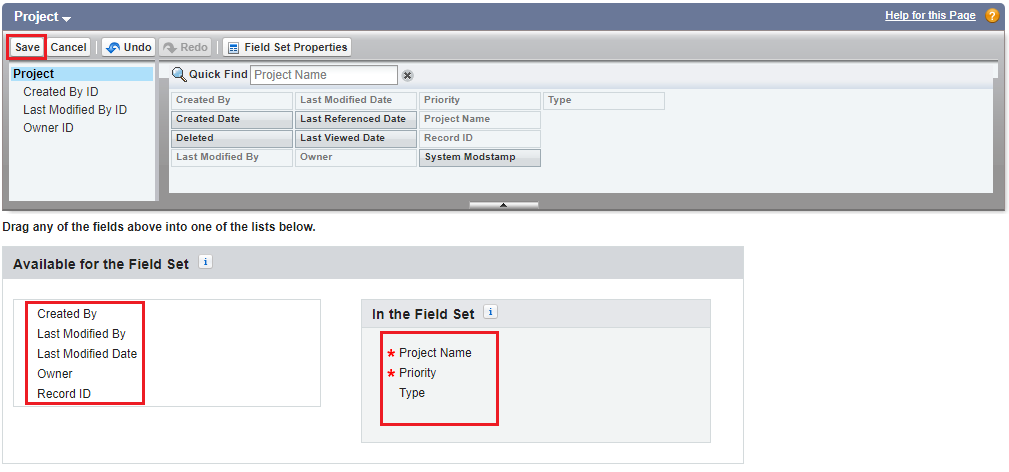
We will get below screen to add fields to field set, where We can drag and drop fields.
Add the necessary fields to field set and save it.
Property of Field Set:
| Property Name |
Description |
| DBRequired |
Indicates whether the field is required for the
object |
| FieldPath |
Lists the field’s spanning info |
| Label |
The UI label for the field |
| Required |
Indicates whether the field is required in the field
set |
| Type |
The data type for the field |
Working with Field Sets Using Visualforce:
Field sets can be directly referenced in Visualforce by combining the $ObjectType global variable with the keyword FieldSets. Here in below Visualforce page the above created Field Set is referenced.
<apex:page standardController="Project__c">
<apex:form>
<apex:pageblock>
<apex:pageblockSection>
<apex:repeat value="{!$ObjectType.Project__c.FieldSets.Project}" var="f">
<apex:inputField value="{!Project__c[f.fieldPath]}" required="{!OR(f.required, f.dbrequired)}"/>
</apex:repeat>
</apex:pageblockSection>
<apex:pageBlockButtons location="bottom">
<apex:commandButton value="Save" action="{!save}"/>
<apex:commandButton value="Cancel" action="{!cancel}"/>
</apex:pageBlockButtons>
</apex:pageblock>
</apex:form>
</apex:page>
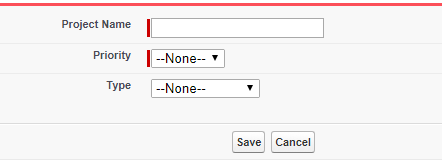
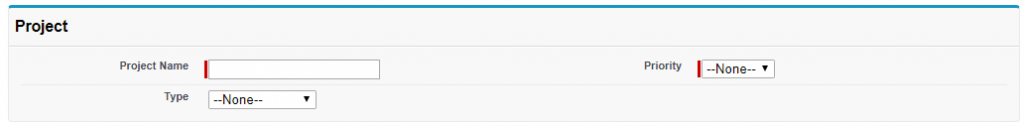
The above code displays all fields in the field set. See the below screen to see the output of above code.
If this Visualforce page is added to a managed package and distributed, subscribers can edit the Project field set. The logic for generating the Visualforce page remains the same, while the presentation differs based on each subscriber’s implementation. To reference a field set from a managed package, you must prepend the field set with the organization’s namespace. Using the markup above, if Project comes from an managed package called TestManagedPackage, the field set is referenced like this:
{!$ObjectType.Project__c.FieldSets.TestManagedPackage__Project}
Working with Field Sets Using Apex:
Fields in a field set are automatically loaded when your Visualforce page uses a standard controller. When using a custom controller, you need to add the required fields to the SOQL query for the page. Apex provides two Schema objects that allow you to discover field sets and the fields they contain, Schema.FieldSet and Schema.FieldSetMember.
Here is an example to display a Field Set on a Visualforce Page using apex.
To dynamically get all the fields from “Project” Field Set we can use Schema.FieldSet and Schema.FieldSetMember methods.
Controller:
public class Sample{
public Project__c proj { get; set; }
public Sample() {
this.proj = new Project__c();
}
public List<Schema.FieldSetMember> getFields() {
return SObjectType.Project__c.FieldSets.Project.getFields();
}
}
Visualforce Page:
<apex:page controller="Sample">
<apex:form >
<apex:pageBlock title="Project">
<apex:pageBlockSection>
<apex:repeat value="{!fields}" var="f">
<apex:inputField value="{!proj[f.fieldPath]}" required="{!OR(f.required, f.dbrequired)}"/>
</apex:repeat>
</apex:pageBlockSection>
</apex:pageBlock>
</apex:form>
</apex:page>
The above code displays all fields in the “Project” field set. See the below screen to see the output of above code.
Field Set Considerations:
- Fields added to a field set can be in one of two categories:
- If a field is marked as Available for the Field Set, it exists in the field set, but the developer hasn’t presented it on the packaged Visualforce page. Administrators can display the field after the field set is deployed by moving it from the Available column to the In the Field Set column.
- If a field is marked as In the Field Set, the developer has rendered the field on the packaged Visualforce page by default. Administrators can remove the field from the page after the field set is deployed by removing it from the In the Field Set column.
- The order in which a developer lists displayed fields determines their order of appearance on a Visualforce page.